ArangoDB v3.9 reached End of Life (EOL) and is no longer supported.
This documentation is outdated. Please see the most recent version at docs.arangodb.com
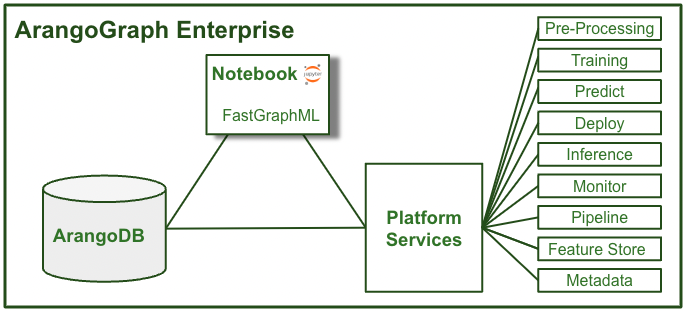
ArangoGraph Notebooks
How to create and manage colocated Jupyter Notebooks within ArangoGraph
This documentation describes the beta version of the Notebooks feature and is subject to change. The beta version is free for all.
The ArangoGraph Notebook is a JupyterLab notebook embedded in the ArangoGraph Insights Platform. The notebook integrates seamlessly with platform, automatically connecting to ArangoGraph services, including ArangoDB and the ArangoML platform services. This makes it much easier to leverage these resources without having to download any data locally or to remember user IDs, passwords, and endpoint URLs.
The ArangoGraph Notebook has built-in ArangoGraph Magic Commands that answer questions like:
- What ArangoDB database am I connected to at the moment?
- What data does the ArangoDB instance contain?
- How can I access certain documents?
- How do I create a graph?
The ArangoGraph Notebook also pre-installs python-arango and ArangoML connectors to PyG, DGL, CuGraph, as well as the FastGraphML library, so you can get started right away accessing data in ArangoDB to develop GraphML models using your favorite GraphML libraries with GPUs.
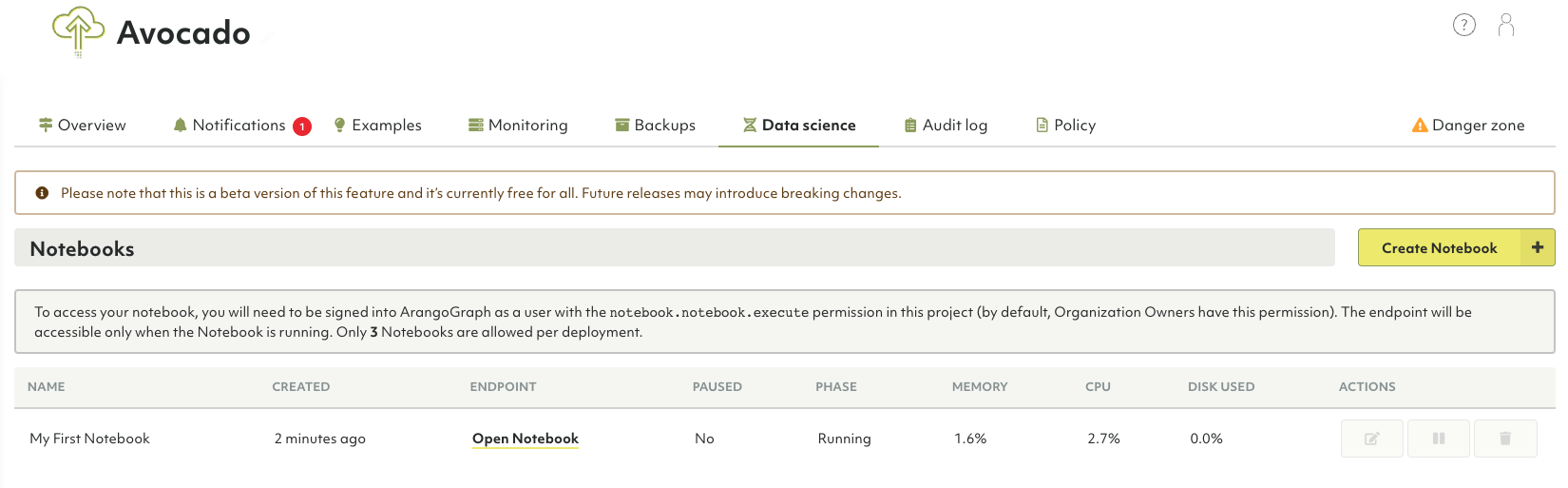
How to create a new notebook
- Navigate to the Deployments tab.
- Open the deployment in which you want to create the notebook.
- Go to the Data science tab and click the Create Notebook button.
- Enter a name and optionally a description for your new notebook.
- Select a configuration model from the dropdown menu. Click Save.
- The notebook’s phase is set to Initializing. Once the phase changes to Running, the notebook’s endpoint is accessible.
- Click the Open notebook button to access your notebook.
- To access your notebook, you need to be signed into ArangoGraph as a user with
the
notebook.notebook.executepermission in your project. Organization owners have this permission enabled by default. Thenotebook-executorrole which contains the permission can also be granted to other members of the organization via roles. See how to create a role binding.
Depending on the tier your organization belongs to, different limitations apply:
- On-Demand and Committed: you can create up to three notebooks per deployment.
- Free-to-try: you can only create one notebook per deployment.
Notebooks in beta version have a fixed configuration of 10 GB of disk size.
How to edit a notebook
- Select the notebook that you want to change from the Notebooks tab.
- Click Edit notebook. You can modify its name and description.
- To pause a notebook, click the Pause notebook button. You can resume it at anytime. The notebook’s phase is updated accordingly.
How to delete a notebook
- Select the notebook that you want to remove from the Notebooks tab.
- Click the Delete notebook button.
Getting Started notebook
To get a better understanding of how to interact with your ArangoDB database cluster, use the ArangoGraph Getting Started template. The ArangoGraph Notebook automatically connects to the ArangoDB service endpoint, so you can immediately start interacting with it.
- Log in to the notebook you have created by using your deployment’s root password.
- Select the
GettingStarted.ipynbtemplate from the file browser.
ArangoGraph Magic Commands
A list of the available magic commands you can interact with.
Single line commands have % prefix and multi-line commands have %% prefix.
Database Commands
%listDatabases- lists the databases on the database server.%whichDatabase- returns the database name you are connected to.%createDatabase databaseName- creates a database.%selectDatabase databaseName- selects a database as the current database.%useDatabase databasename- uses a database as the current database; alias for%selectDatabase.%getDatabase databaseName- gets a database. Used for assigning a database, e.g.studentDB=getDatabase student_database.%deleteDatabase databaseName- deletes the database.
Graph Commands
%listGraphs- lists the graphs defined in the currently selected database.%whichGraph- returns the graph name that is currently selected.%createGraph graphName- creates a named graph.%selectGraph graphName- selects the graph as the current graph.%useGraph graphName- uses the graph as the current graph; alias for%selectGraph.%getGraph graphName- gets the graph for variable assignment, e.g.studentGraph=%getGraph student-graph.%deleteGraph graphName- deletes a graph.
Collection Commands
%listCollections- lists the collections on the selected current database.%whichCollection- returns the collection name that is currently selected.%createCollection collectionName- creates a collection.%selectCollection collectionName- selects a collection as the current collection.%useCollection collectionName- uses the collection as the current collection; alias for%selectCollection.%getCollection collectionName- gets a collection for variable assignment, e.g.student=% getCollection Student.%createEdgeCollection- creates an edge collection.%createVertexCollection- creates a vertex collection.%createEdgeDefinition- creates an edge definition.%deleteCollection collectionName- deletes the collection.%truncateCollection collectionName- truncates the collection.%sampleCollection collectionName- returns a random document from the collection. If no collection is specified, then it uses the selected collection.
Document Commands
%insertDocument jsonDocument- inserts the document into the currently selected collection.%replaceDocument jsonDocument- replaces the document in the currently selected collection.%updateDocument jsonDocument- updates the document in the currently selected collection.%deleteDocument jsonDocument- deletes the document from the currently selected collection.%%importBulk jsonDocumentArray- imports an array of documents into the currently selected collection.
AQL Commands
%aql single-line_aql_query- executes a single line AQL query.%%aqlm multi-line_aql_query- executes a multi-line AQL query.
Variables
_endpoint- the endpoint (URL) of the ArangoDB Server._system- the system database used for creating, listing, and deleting databases._db- the selected (current) database. To select a different database, use%selectDatabase._graph- the selected (current) graph. To select a different graph, use%selectGraph._collection- the selected (current) collection. To select a different collection, use%selectCollection._user- the current user.
You can use these variables directly, for example, _db.collections() to list
collections or _system.databases to list databases.
You can also create your own variable assignments, such as:
schoolDB=%getDatabase schoolDBschool_graph=%getGraph school_graphstudent=%getCollection Student
Reset environment
In the event that any of the above variables have been unintentionally changed,
you can revert all of them to the default state with reset_environment().

