ArangoDB v3.8 reached End of Life (EOL) and is no longer supported.
This documentation is outdated. Please see the most recent version at docs.arangodb.com
Web Interface
The server itself (arangod) speaks HTTP / REST, but you can use the graphical web interface to keep it simple. There is also arangosh, a synchronous shell for interaction with the server. If you are a developer, you might prefer the shell over the GUI. It does not provide features like syntax highlighting however.
When you start using ArangoDB in your project, you will likely use an official or community-made driver written in the same language as your project. Drivers implement a programming interface that should feel natural for that programming language, and do all the talking to the server. Therefore, you can most certainly ignore the HTTP API unless you want to write a driver yourself or explicitly want to use the raw interface.
To get familiar with the database system you can even put drivers aside and
use the web interface (code name Aardvark) for basic interaction.
The web interface will become available shortly after you started arangod.
You can access it in your browser at
http://localhost:8529 - if not, please
see Troubleshooting.
By default, authentication is enabled. The default user is root.
Depending on the installation method used, the installation process either
prompted for the root password or the default root password is empty
(see Securing the installation).
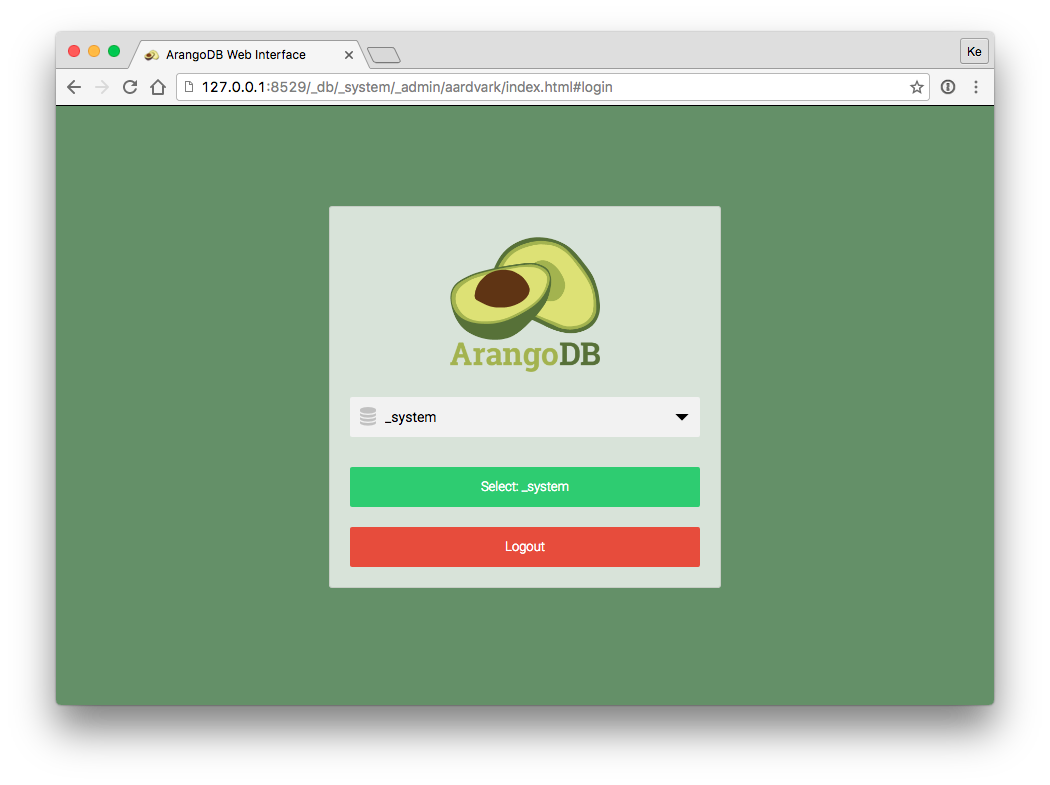
Next you will be asked which database to use. Every server instance comes with
a _system database. Select this database to continue.
You should then be presented the dashboard with server statistics like this:
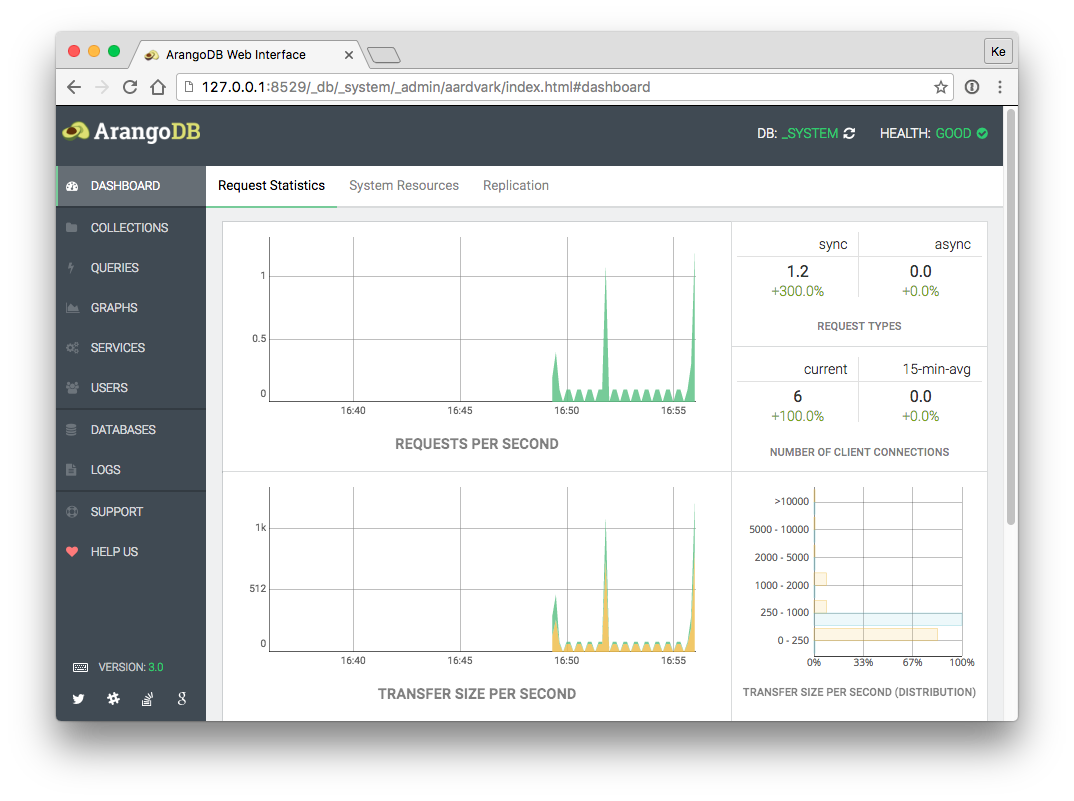
For a more detailed description of the interface, see Web Interface.

